|
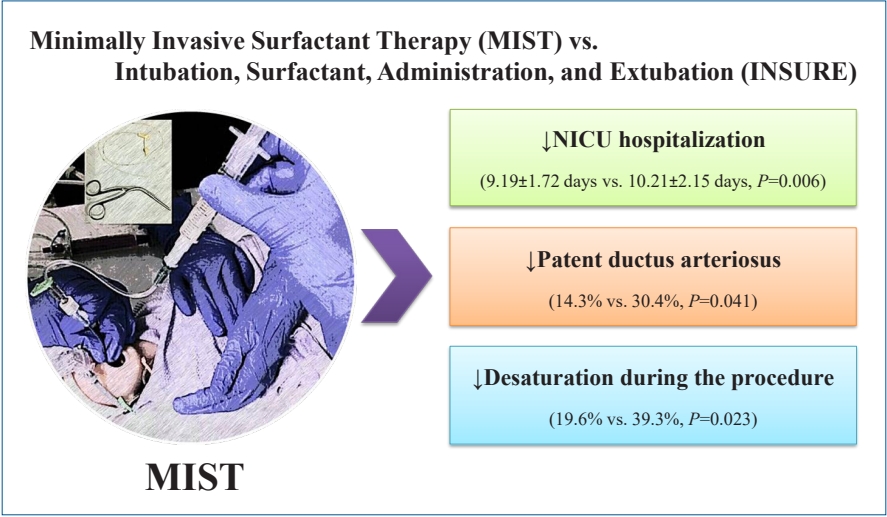
Question: Are the short-term outcomes of minimally invasive surfactant therapy (MIST) relatively superior to those of INtubation, SURfactant administration, and Extubation (INSURE) in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)?
Finding: MIST could be an appropriate substitution for INSURE in preterm infants with RDS since it reduced hospitalization time and number of side effects.
Meaning: MIST is recommended for surfactant administration for its proven advantages over the INSURE technique. |






